Nasal Cavity Function Describe. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. The nasal cavity has four functions: What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Warms and humidifies the inspired air.
Nasal Cavity Function Describe . The Framework Of The Nose Consists Of Bone And Cartilage.
Final Lecture Exam. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal cavity has four functions: In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study.
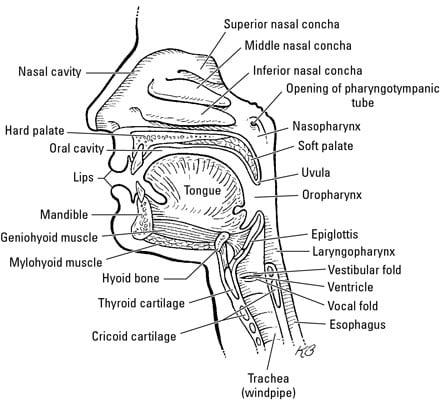
Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract.
Structures within the cavity regulate the flow of air and particles it contains. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. Nasal cavities have several functions. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. The inside of the nose (also. Nasal bone and cartilage palpation. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. Want to learn more about it? The nasal cavity forms part of the aerodigestive tract. The perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of the ethmoid and the inferior concha. Inferior, middle and superior nasal conchae (turbinates) superiorly: Cribriform plate of the ethmoid. The nasociliary branch of v1 gives off two. The lateral wall of the nasal cavity is mainly made up by the maxilla, however there is a deficiency that is compensated by: The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. In addition, the epithelium lining the trachea produces mucus that traps dust and other. Other articles where nasal cavity is discussed: In addition to getting comprehensive answers to all these questions, here you will also learn about the structure, anatomy and functions of the nasal cavity.lots of interesting facts about nose and nasal cavity are also given. …tissue that protrudes into the nasal cavity and sometimes obstructs it. The main function of the trachea is to provide a clear airway for air to enter and exit the lungs. Haghighat on nasal cavity function: The nasal cavity heats and humidifies the inspired air and filters small particles into the air before the air reaches the lung. Helpful, trusted answers from doctors: The nasal cavity (or nasal fossa) is a large air filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. There are many different benign and malignant tumors of the nasal cavity/nasopharynx, though outside of common polyps, they are. The nasal cavity functions to allow air to enter the respiratory system upon respiration. Gross anatomy the nasal cavity is formed by 1: The framework of the nose consists of bone and cartilage. The other stages range from i (1) through iv the staging system most often used for nasal cavity and paranasal sinus cancers is the american joint committee on cancer (ajcc) tnm system. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels.
Respiratory System Wikipedia , In Addition, The Epithelium Lining The Trachea Produces Mucus That Traps Dust And Other.
Final Lecture Exam. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal cavity has four functions: It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Nasal Cavity Inner Nose And Mucosa Myvmc : Warming Of Air 4 Describe In Detail The V1 Nerves That Supply The Nose?
Nose Ulcer An Overview Sciencedirect Topics. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. The nasal cavity has four functions: What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat.
Respiratory System Wikipedia : The nasal cavity forms part of the aerodigestive tract.
Respiratory System Wikipedia. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The nasal cavity has four functions: Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels.
Nasal Cavity Definition Anatomy Functions Diagrams : The Goal Of The Surgery Is To Remove Your Nasal Cavity And Sinuses Are Small Areas That Have Many Muscles, Nerves, Blood Vessels, And The Different Types Of Surgery Are Described Below.
Functions Of Nasal Cavity Brainly In. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. The nasal cavity has four functions: Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram.
Nasal Cavity Definition Of Nasal Cavity By Medical Dictionary Sinusitis Sinus Infection Nasal Cavity - The Sinus, Or Nasal Cavity, Serves To Lighten The Skull, To Produce Mucus, To Warm And Moisturize Air Breathed In When The Air Is Exhaled, The Sinuses Trap Some Of The Moisture And Warmth On The Way Out, Ensuring The Cavities Remain At The Optimal Temperature For Treating The Next Incoming Breath.
5 Functions Of Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. The nasal cavity has four functions: Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils.
Functions Of Nasal Cavity Brainly In - Nasal Cavities Have Several Functions.
Rhinopharyngitis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The nasal cavity has four functions: The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of.
Chapter 22 Respiratory System 1 . The Mucosa Of The Nasal Cavity Is Well Supplied With Blood Vessels.
Anterior Cranial Fossa Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The nasal cavity has four functions: Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air.
Lecture 15 Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Bisc 3112 Studocu : Airborne Particles Are Filtered Out By The Mucosal Surface, And Thereby Prevented From Reaching The Lungs.
Nasal Cavity Anatomy Structure Parts Blood Supply Kenhub. The nasal cavity has four functions: The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy.
Nasal Cavity Paranasal Sinuses Flashcards Quizlet - Inferior, Middle And Superior Nasal Conchae (Turbinates) Superiorly:
Nasal Cavity Arterial Supply And Nasal Meatuses And Chonchae Anatomy Qa. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. The nasal cavity has four functions: The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system.
Nasal Passageway Microbewiki , Large, Thin Walled Veins Can Be Seen In The The Tissue Has Been Described As Erectile, And Marked Swelling Of The Mucosa Can Be Produced By Engorgement Of.
21 2a Nose And Paranasal Sinuses Medicine Libretexts. Arteries enter the cavity through the sphenopalatine and incisive foramina. The nose and nasal cavity make up the first portion of the upper respiratory tract. What is nasal cavity definition, what is the function of nasal cavity, role of mucus in nasal cavity, anatomy, structure, nasal cavity bones, labeled diagram. The nasal cavity is an anatomical formation, which originates in the respiratory system. The nasal cavity has four functions: The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Nasal cavity facts, function, parts and diseases, a comprehensive study. It runs a number of processes that provide the moisturizing, cleaning and heating of inhaled air. In addition, it performs other vital functions due to its complex anatomy. Large, thin walled veins can be seen in the the tissue has been described as erectile, and marked swelling of the mucosa can be produced by engorgement of. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal and oral cavities are connected with each other through the nasopharynx at the back of the throat. Their locations and structures are best viewed when the head is shown in sagittal inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The mucosa of the nasal cavity is well supplied with blood vessels.