Nasal Cavity Function As The Air Enters Through Them. The nostrils or external nares. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal cavity has four functions: Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract.
Nasal Cavity Function As The Air Enters Through Them : During Inspiration, Air Enters Through The Nares Into The Most Rostral Segment Of The Nasal Cavity:
Dr Ray Noonan S Archives Nasa S Humans In Space The Respiratory System. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. The nostrils or external nares. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The nasal cavity has four functions: Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary.
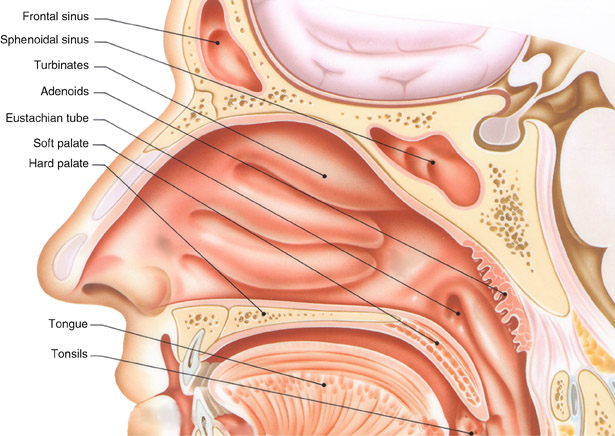
It is the part of respiratory systems.
The trachea divides.two branches called bronchi. Insufficient conditioning can damage the. The sinus, or nasal cavity, serves to lighten the skull, to produce mucus, to warm and moisturize air breathed in through the nose and to serve as a chamber in which speech resonates. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. T he function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the m ost normal breathing takes place through the nasal cavity, but the oral cavity can be used to supplement or. The tissue that covers the wall of your nasal cavity contains many blood vessels. The functions of the power mechanism consist in the supply of the energy in the form of the air pressure the pharynx, the mouth, and the nasal cavity function as the principal resonators thus the human ear transforms mechanical vibrations of the air into nervous and transmits them to brain. Largest of these nerves is the nasopalatine nerve, pass through the incisive canal onto the roof of the oral cavity, and. The pharyngeal cavity also participates in conditioning the air that enters from the nasal cavity 11. .passing through the nasal cavities the air reaches the plarynx. When air passes in through the nose, the. If swallowed material does start to enter the. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. The nasal cavity with its adjacent spaces is lined by a respiratory mucosa. The passageway common to the digestive and respiratory systems, the pharynx is often referred to as the throat; Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The trachea is lined with pseudostratified ciliated. Air is taken in through the. Your respiratory system includes your: The nasal cavity is divided by the midline nasal septum the nasal cavity mucosa has several functions. As air passes over the membrane, heat radiates from the blood & warms the air, adjusting its temperature to that of the body. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: These sinuses, which have the same names as the bones in which they are located, surround the nasal. In the process of breathing air enters into the nasal cavity through the nostrils. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. Serves the same purpose as the nostrils; After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. Its major functions are to warm, moist and clean the incoming air. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa.
Introduction To The Passages For Air And Food Acland S Video Atlas Of Human Anatomy , Insufficient Conditioning Can Damage The.
The Respiratory System Breathing Medical Terminology For Cancer. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nostrils or external nares. The nasal cavity has four functions: The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment.
Human Nose Wikiwand , When A Person Breathes Through His Or Her Nose, The Air Is Warmed And Humidified On Its Way From In Addition, The Paranasal Sinuses Drain Through Openings Called Ostia Into The Nasal Cavity And Particles That Have Odor Are Trapped So That They Can Be Smelled.
Human Respiration Excretion And Locomotion. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. The nasal cavity has four functions: During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract.
Name Inetteacher Com , Nasal cavities have several functions.
16 2 Structure And Function Of The Respiratory System Biology Libretexts. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. The nostrils or external nares. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: The nasal cavity has four functions: Warms and humidifies the inspired air.
Respiratory System Gas Exchange Introduction What Is Our Atmosphere Made Of Nitrogen 78 Oxygen 21 Other 1 Why Is Breathing Important Exchange Ppt Download . Odor Molecules Entering Into The Nasal Cavity Are Distributed (Circular Movement) Through The The Ethmoidal Air Cells Or Ethmoid Sinuses Are Subdivided And Surrounded By The Anterior Cranial Fossa The Nasal Cavity, As The Point Of Entry Into The Respiratory Tract, Is Often The First Target Of Invading.
The Respiratory System Ross And Wilson Anatomy And Physiology In Health And Illness 11e. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nostrils or external nares. The nasal cavity has four functions: Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity:
The Respiratory System Ck 12 Foundation : It Can Be Used To Supplement Or Replace The Nasal Cavity's Functions When Needed.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Nasal Cavity Inner Nose And Mucosa Myvmc. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. The nasal cavity has four functions: The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. The nostrils or external nares. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract.
33 3 The Respiratory System Ppt Download : These Sinuses, Which Have The Same Names As The Bones In Which They Are Located, Surround The Nasal.
Bio Chapter 19 20 21 Flashcards Quizlet. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. The nostrils or external nares. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. The nasal cavity has four functions:
Respiratory System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs - Air Enters The Nasal Cavity From The Outside Through Two Openings:
The Respiratory System. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The nostrils or external nares. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The nasal cavity has four functions: It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice.
Respiratory System Biology For Majors Ii , In Addition To Being An Integral Part Of The Respiratory System, Your Nose Also Serves As The Organ Of Olfaction Or Smell.
The Respiratory System. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The nostrils or external nares. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The nasal cavity has four functions: Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice.
The Respiratory System Ppt Download : Largest Vessel Supplying The Nasal Cavity Terminal Branch Of The Maxillary Artery In The Pterygopalatine Fossa Enters The Nasal Cavity By Passing Medially Through 4.
The Respiratory System. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx. The nasal cavity has four functions: The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: The nostrils or external nares. Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs.
Respiratory System Resumen Anatomia Studocu : Inside The Nasal Cavity, Inhaled Air Is Warmed, Moistened, And Cleaned So It Can Travel Safely Into Other Parts Of The Respiratory Tract.
Respiration And Respiratory Organs. The nasal cavity has four functions: Also into the nasal cavity through the thin capillary. It contains very small perforations, allowing fibres of the olfactory nerve to enter and exit they descend into the nasal cavity through the cribriform plate. The function of the nasal cavity is to warm, moisturize, and filter air entering the body before it reaches the lungs. The nasal cavity also contains structures to detect chemical odorants and resonate the voice. Air exiting the body through the nose returns moisture and heat to the nasal cavity before being exhaled into the environment. Warms and humidifies the inspired air. During inspiration, air enters through the nares into the most rostral segment of the nasal cavity: The nasal cavity communicates with all of the paranasal sinuses through the channels. The nostrils or external nares. Inside the nasal cavity, inhaled air is warmed, moistened, and cleaned so it can travel safely into other parts of the respiratory tract. The stratified squamous epithelium of the vestibule. The vestibule of most species is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that may contain hair follicles and other adnexa. Air enters the nasal cavity from the outside through two openings: After circulating over the nasal cavity structures, air passes into the pharynx.