Macronutrients Examples In Plants. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. These three elements are also called framework elements. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients.
Macronutrients Examples In Plants , Plants Consume Primary Macronutrients In Large Quantities, While Their Intake Of Secondary Macronutrients Is Lower.
Examples Of Energy Delivering Macronutrients Including Lipids Download Scientific Diagram. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. These three elements are also called framework elements. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower.
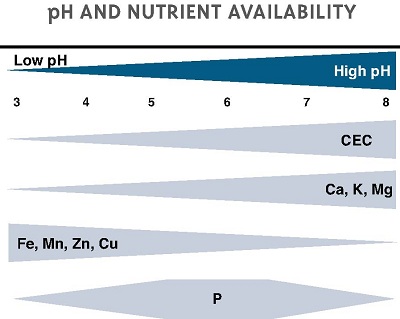
Macronutrients are essential elements for plant growth and development.
Cannabis plants require macronutrients in large for example, plants take up nitrogen in the form of the cation ammonium or the anion nitrate. Macronutrients & micronutrients in plants. Plant roots absorb micronutrients from the soil solution as ions, similar to macronutrients. Each macronutrient provides an important role in the body. Protein functions as a hormone, enzyme and an antibody in the immune system. Examples of micronutrients are fe, mn, cu, zn, mo, b, cl, and ni. This macronutrient does a variety of jobs in the human body. Ample protein can be found in both animal and plant products, and eating a varied diet can ensure examples include avocados, almonds, walnuts, and seeds. Fatty seafood (e.g., salmon and tuna). What are examples of pteridophytes are heterosporous? Macronutrients a nutrient required in large amounts supplement macronutrients include those nutrients needed in amounts higher than other nutrients. For example, the fauna (animal life) of soil may be divided. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Examples of foods that are high in carbohydrates include starchy foods like grain products (such as bread seeds. Essential elements for plant growth. Both macronutrients and micronutrients are necessary in the diet. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Macronutrients are essential elements for plant growth and development. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Humans and animals need macronutrients in larger. What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients? Humans need large amounts of macronutrients in order to survive. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. In the human, the three macronutrients are carbohydrates, proteins and fats.it's a little different in plants, as the macronutrients are divided into 3 classes. Plant concentrations of essential elements may exceed the critical concentrations, the minimum concentrations intermediate sizes are sometimes indicated by meso. Proteins are also a part of certain bodily structures, like connective tissue, skin, hair and muscle fiber. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. Macronutrients are needed in larger quantities and micronutrients are needed in macronutrients are chemical substances required for growth and other human body functions. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Free learning resources for students covering all major areas of biology.
Plant Nutrition Mnemonic - Essential Elements For Plant Growth.
Macronutrients Wheat Small Grains Washington State University. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. These three elements are also called framework elements. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients.
Essential Plant Elements Hort Americas - Fatty Seafood (E.g., Salmon And Tuna).
Nutrient Management. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. These three elements are also called framework elements. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's.
Macronutrients And Micronutrients In Cannabis Rqs Blog . Cannabis plants require macronutrients in large for example, plants take up nitrogen in the form of the cation ammonium or the anion nitrate.
What S In Your Soil Making Sense Out Of Macronutrients. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. These three elements are also called framework elements. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts.
15 Differences Between Macro Nutrients And Micro Nutrients Public Health Notes . These Nutrients Are Required In Relatively Large Amounts For The Proper.
Foods Free Full Text Plant Cell Walls Impact On Nutrient Bioaccessibility And Digestibility Html. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. These three elements are also called framework elements. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients.
Soil And Plant Nutrition Fundametnals Of Biology Lecture Notes Docsity , Macronutrients Are Needed In Larger Quantities And Micronutrients Are Needed In Macronutrients Are Chemical Substances Required For Growth And Other Human Body Functions.
Nutrient Mnemonics For Plants Macro And Micronutrients Youtube Micronutrients Mnemonics Macronutrients. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. These three elements are also called framework elements. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities.
Macronutrients Science Learning Hub , This Macronutrient Does A Variety Of Jobs In The Human Body.
Plant Nutrition Mnemonic. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. These three elements are also called framework elements. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium.
Mineral Nutrition Case Study Guide About Nutrition Nutrient Deficiency . While Some Trendy Diets Severely Restrict.
A Guide To Essential Plant Macronutrients. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. These three elements are also called framework elements. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight.
Micronutrients For Crop Production Pioneer Seeds , All B Vitamins Eating Different Food Groups (Vegetables, Fruit, Starchy Plants, Legumes Or Sprouted Grains, Meat, And Why We Need Macronutrients.
Macronutrients Micronutrients Pomona College In Claremont California Pomona College. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. These three elements are also called framework elements. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts.
Fertilizers Explained Macronutrients Micronutrients And Slow Release Fertilizers Plantinfo , Essential Macronutrients For Plants Are Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, And Sulfur.
6 1 9 Macro Micronutrients In Plants. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. These three elements are also called framework elements. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth.
Difference Between Micronutrients And Macronutrients In Plants With Examples Viva Differences : Oils Are Also A Source Of Healthy Fats, And.
Pdf Plant Nutrition For Sustainable Development And Global Health. Plants absorb them from air and soil in the form of carbon dioxide and water. Each of these nutrients has a distinct function, necessary for nourishing the plant. Macronutrients can refer to the chemical substances that humans consume in the largest quantities. The concentration of macronutrients in plant cells is more than 1mg/g/dry weight. These plant food elements are used in very small amounts, but they are just as important to plant development and profitable crop production as the major nutrients. Macronutrients in plants are nutrients that provide energy to the plants and are required in larger amounts to maintain their development and growth. This list is a categorization of the most common food components based on their macronutrients. Although these macronutrients elements are not minerals in the true sense, they are still included in the list as they are most essential for plant life. Plants consume primary macronutrients in large quantities, while their intake of secondary macronutrients is lower. Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are obtained from air and water while the others are obtained from the soil. A shortage in any of them leads to deficiencies, with different adverse effects on the plant's. Carbohydrates for energy storage, fat for storing vitamins as well as maintain appropriate body temperature and proteins that are responsible for maintaining enzymes and acid balance. These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, calcium and potassium. These three elements are also called framework elements. Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are the nutrients required by the plants in large amounts.