Barrett's Esophagus Gross. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. How is low grade dysplasia. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux.
Barrett's Esophagus Gross - Gastric Mucosa With Intestinal Metaplasia, Consistent With Barrett.
Identification Of Prognostic Phenotypes Of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma In 2 Independent Cohorts Gastroenterology. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. How is low grade dysplasia. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux.
Barrett's esophagus is a condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth to the stomach.
Barrett's esophagus is a condition marked by an abnormality in the lining of the lower esophagus. Barrett's esophagus slightly increases the risk of developing a cancer called esophageal adenocarcinoma. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Since barrett's esophagus is a known precursor to esophageal cancer (or esophageal adenocarcinoma ) — which is a very difficult cancer to fight if not treated early enough. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. How is low grade dysplasia. Learn more from webmd about barrett's esophagus, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. Whereby normal stratified squamous epithelium is replaced by simple columnar epithelium. Acid reflux (gerd) contributes to its development, but you can have the disorder without having gerd. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. In barrett esophagus, healthy esophageal epithelium is replaced with metaplastic columnar cells—the result, it is believed, of damage from prolonged exposure of the esophagus to the refluxate of. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? 4 natural ways to manage barrett's esophagus. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Barrett's esophagus occurs when cells in the lining of the esophagus are damaged by exposure to acid this condition often develops after years of experiencing gastroesophageal reflux (gerd). In barrett's oesophagitis or barrett's oesophagus cells that line the lower gullet are abnormal. Barrett's esophagus is a condition affecting the lining of the esophagus, the swallowing tube that carries foods and liquids from the mouth to the stomach. The new cells take over because the lining of the esophagus has been. Doctors can treat the tissue changes linked to barrett's esophagus with surgery. Barrett's oesophagus refers to metaplasia of the oesophageal epithelial lining; Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). It is believed to be due to severe, longstanding, gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a change in the cells lining your esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a rare, irreversible condition characterized by changes in the internal lining of the esophagus (food pipe). Symptoms of barrett's oesophagus are usually no different from regular heartburn and may seem insignificant. Risk factors for barrett's esophagus among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Barrett's esophagus is when the normal cells that line your food pipe (esophagus) turn into cells not usually found in your body.
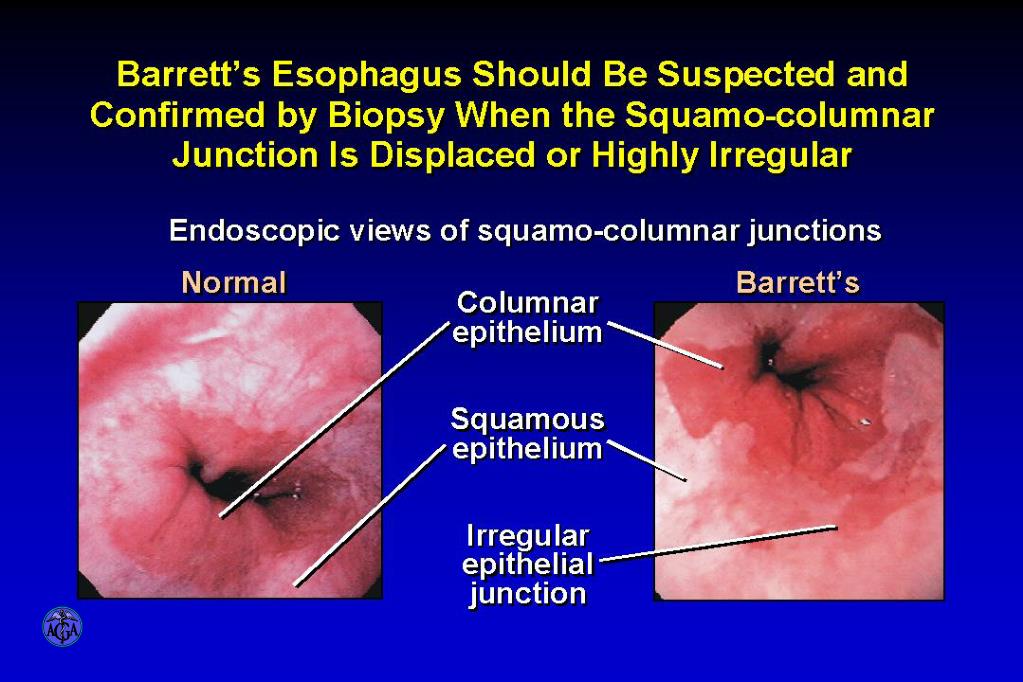
Ppt Esophagus Normal Lower Esophageal And Squamo Columnar Junction Mucosae Powerpoint Presentation Id 1074687 . Endoscopic Diagnosis Of Barrett Esophagus — Can Barrett Esophagus Be Diagnosed.
Barrett S Oesophagus For The Histopathologist. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. How is low grade dysplasia. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus.
A Computer Assisted Algorithm For Narrow Band Imaging Based Tissue Characterization In Barrett S Esophagus Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Whereby Normal Stratified Squamous Epithelium Is Replaced By Simple Columnar Epithelium.
Duke Pathology Gastrointestinal Tract. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to.
Figure 1 From Evaluation Of Dysplasia In Barrett Esophagus Semantic Scholar . Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to.
Git Pathology M Scyear2011 12. How is low grade dysplasia. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Columnar epithelium lined lower (o).
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Gerd And Barrett S Esophagus Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Barretts Esophagus Reflux Disease . 4 Natural Ways To Manage Barrett's Esophagus.
Pathology Outlines Adenocarcinoma. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. How is low grade dysplasia. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus:
Esophagus At Ross University School Of Medicine Studyblue , For This Reason, Many People Don't Seek Medical Treatment Until Their Condition Is Quite.
Barrett S Esophagus Wikipedia. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. How is low grade dysplasia. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus.
Diseases Of The Esophagus Flashcards Quizlet - In Barrett Esophagus, Healthy Esophageal Epithelium Is Replaced With Metaplastic Columnar Cells—The Result, It Is Believed, Of Damage From Prolonged Exposure Of The Esophagus To The Refluxate Of.
Ppt Esophagus Normal Lower Esophageal And Squamo Columnar Junction Mucosae Powerpoint Presentation Id 1074687. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. How is low grade dysplasia. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett.
Pathology Chapter 17 And 19 Images Flashcards Cram Com : Barrett's Esophagus Is A Condition In Which The Lining Of The Esophagus Changes, Becoming More Like The Lining Of The Small Intestine Rather Than The Esophagus.
Path Spring Gi Skin Repro Flashcards Memorang. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. How is low grade dysplasia. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd).
Barrett S Esophagus Bpa Pathology . For This Reason, Many People Don't Seek Medical Treatment Until Their Condition Is Quite.
Barrett S Oesophagus Stock Image M120 0183 Science Photo Library. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. How is low grade dysplasia. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus.
8 Esophagus Stomach 1 Barrett Esophagus Pathology Core Pictures : The Condition Is Recognized As A Complication Of Gastroesophageal Reflux.
Pathology Of The Esophagus Pathology Flashcards Memorang. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux. Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. How is low grade dysplasia.
Esophagus At Ross University School Of Medicine Studyblue - The Condition Is Recognized As A Complication Of Gastroesophageal Reflux.
Pdf Barrett S Esophagus Review Of Diagnosis And Treatment. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from normal stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet cells that are normally present only in the small intestine. Gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia, consistent with barrett. Columnar epithelium lined lower (o). Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the lining of the esophagus changes, becoming more like the lining of the small intestine rather than the esophagus. What does endoscopic biopsy surveillance in barrett's esophagus involve? How is low grade dysplasia. Barrett's esophagus is the condition in which a metaplastic columnar epithelium that has both gastric and intestinal features barrett's esophagus: Пищевод барретта (синдром барретта — англ. (1999) management of barrett's esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which columnar cells replace the usual squamous cell in the mucosa of the esophagus. Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd). Screening for barrett's esophagus in colonoscopy patients with and without heartburn. Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which the flat pink lining of the swallowing tube that connects the mouth to the stomach (esophagus) becomes damaged by acid reflux, which causes the lining to. Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnosis. The condition is recognized as a complication of gastroesophageal reflux.